Personally identifiable information (PII) should always be top of mind for relevant organisations. This sensitive data is central to security laws and regulations around the world.
It’s critical that you are always aware of the current state of your website’s data protection and the data you are storing. This enables you to comply with data regulations.
That’s why PII scanning is so important. This guide will take you through PII scanning, including tools and methods you can use for optimal results.
It is the ideal place to start for businesses attempting to comply with data protection regulations.
What is PII?
Personally identifiable information is any kind of data that can be used to identify an individual. Forms of data considered to fall into this category include:
- Name
- Signature
- Address
- Phone number
- Date of birth
- Driver’s licence
- Passport information
- Credit card data
- Photographs
- IP address
- Biometric data
- Location information
- Email address
- Social security number
Businesses store PII in a variety of ways, including on servers, computers and paper documents.
What is PII scanning?
PII scanning is a process undertaken to discover the PII that your business is accumulating. Your business is likely to be storing PII without even intending to.
That’s why the process of PII scanning is so important. If you don’t know what PII you are responsible for, you cannot dispose of it or secure it in-line with relevant regulations.
Your business may have accumulated PII via the following methods:
- Digital forms filled out by customers
- E-commerce POS systems
- Internal tags and cookies
- Analytics tools
- Customer relationship management software
- Communications with your customer support
- Chatbots
With so many potential avenues for PII to be collected, it is essential that your business take steps to understand the personal and sensitive data you are responsible for.
When should you use a PII scanning tool?
You should use PII scanning tools if you are at all unsure what PII your business is responsible for. That means if you’ve never conducted a PII audit before, you should move it to the top of your priority list.
You may also wish to conduct a PII scan if you are conducting a general data audit. For example, if your business has recently suffered a data breach, a PII scan is an essential part of reconfiguring your security procedures.
Complying with the General Data Data Protection Regulation
One of the most significant data privacy regulations in the world is the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation. The GDPR applies to virtually any business which targets EU citizens with products and services, or otherwise processes the data of EU citizens.
That means if it is possible for EU citizens to access your site, you should aim to comply with the GDPR.
The GDPR lays out 7 principles for businesses to follow:
- Lawfulness, fairness and transparency
- Purpose limitation
- Data minimisation
- Accuracy
- Storage minimisation
- Integrity and confidentiality (security)
- Accountability
When it comes to PII scanning, 3 principles to underline are purpose limitation, data minimisation and integrity and confidentiality.
Taken together, the principles of purpose limitation and data minimisation mean that your business should be collecting and storing the minimum amount of data necessary for your operations. As such, PII scanning may turn up large quantities of data you should lawfully dispose of.
Integrity and confidentiality mean that data must be stored in a secure way. Steps must be taken to protect customer data from potential internal and external threats.
These principles should guide your approach to PII scanning and the subsequent actions your business takes.
The GDPR also lays out Data Subject Access Requests. These requests mean that customers have the right to know exactly what data of theirs is being collected and retained by businesses.
In order for you to fulfil a DSAR, you naturally must be aware of the data you are storing. This is yet another reason why PII scanning is so significant.
PII scanning checklist
By now, you are likely extremely eager to begin the PII scanning process. Below are the steps you need to take to detect sensitive data accurately and proceed appropriately:
1. Conduct a physical audit
Before entering the digital realm, your business should go over the data which you are physically storing. Build a physical sensitive data inventory for your business.
Some physical documents which may include PII are:
- Sign-up sheets
- Surveys
- Invoices
- Receipts
A commonality in data privacy regulations is that PII collection should be kept to a minimum. As such, it is worth considering whether collecting data in this way is a necessity for your business. If not, it should be lawfully disposed of.
2. Take stock of devices and servers
Create a list of all computers, mobile devices, flash drives and other devices which could contain PII. Consider all the ways your business receives and stores PII. Then, figure out which devices may be storing PII and add them to your inventory.
You will need to create a similar inventory of servers your business is using. Find any servers you control and add them to your PII watchlist.
3. Conduct a PII scan for devices and servers
Some of the PII stored on devices and servers will be easy to locate. Other pieces of PII can be much harder to identify.
This is why PII scanning tools are a necessity. There are many tools out there for data discovery.
Some can even be used to interpret more inscrutable files such as images of handwritten notes. You will need to conduct these scans for devices as well as on servers.
4. Conduct a tag and cookie audit
To fully understand all the data your business is responsible for, you need to audit your tags and cookies. This will identify other data that may be lurking on your devices or first-party servers.
It can also highlight PII that is being sent to third-party servers. Regulations for sharing PII with third parties are extremely tight. It’s essential you know exactly where your data is being sent.
The good news is, if you’ve got a DataTrue Enterprise subscription, you’ve got a number of tools for alerting you of potential breaches, even if you haven’t thought about them yet. Whenever you run a Simulation Test in DataTrue, it also scans for PII, in addition to any tags you’ve specified.
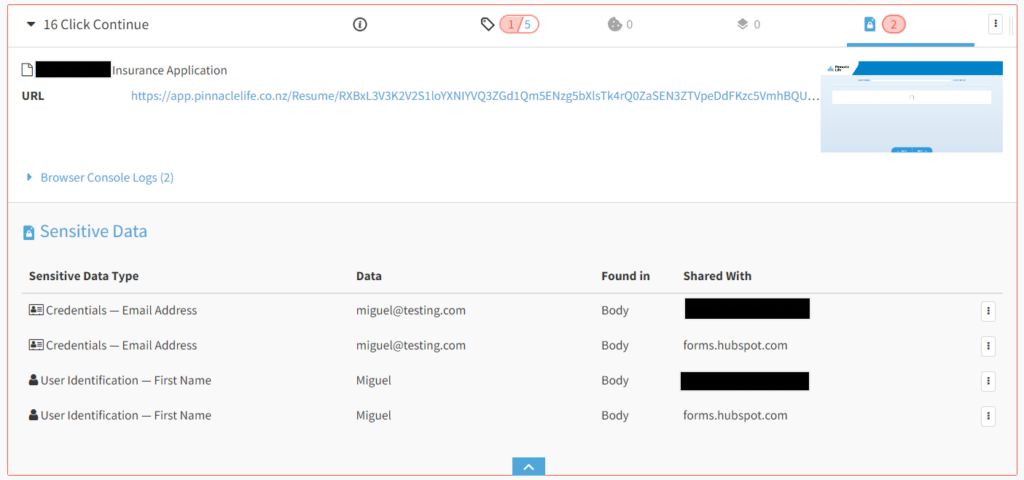
That’s just one part of DataTrue’s tag analytics toolset. You can monitor tags across your web analytics, mobile analytics and email analytics. This helps to ensure holistic data compliance.
Another important element of PII scanning is a cookie audit. Some cookies used by you and by third parties can be difficult to locate.
This can lead to your business unintentionally accumulating PII. Fortunately, cookie audits help you catch a comprehensive breadth of cookies on your site. DataTrue offers enhanced cookie discovery on top of its cookie policy audit functionality.
DataTrue does much more than ensure your business is making decisions based on the best data. It also has a wide range of functions to keep your data usage compliant.
5. Secure or dispose of data
At this stage, you are aware of customer data which is:
- Stored in physical formats
- Stored on computers and first-party servers
- Being sent to third-party servers
You must now secure or dispose of this data. The GDPR and other regulations provide plenty of direction on the correct ways to go about doing this.
First, you’ll need to decide whether it is appropriate to secure or dispose of PII. The GDPR and other regulations emphasise the importance of minimising the collection of PII wherever possible.
PII should be collected only when necessary for the function of the business. Retention of PII should also be limited where possible. That means it should only be stored for as long as is necessary.
Securing PII
Here are some of the steps your business can take to ensure PII is stored securely:
- Ensure data is stored on first-party servers with extensive security policies.
- Encrypt PII wherever possible.
- Establish strong access controls. Follow the principle of least privilege, meaning employees only access data that is totally necessary for them to do their jobs.
- Train staff on how to handle sensitive data.
- Install high-level malware protection on devices and servers.
Disposing of PII
What about the data you do not need to retain? You need to dispose of it in a lawful way. Fundamentally, this means that when data is destroyed, it should be destroyed for good.
For physical paper files, use paper shredders to destroy them. For digital files, you must delete them securely.
That means emptying the recycle bin won’t cut it. Use specialised software to delete your files permanently.
6. Set future processes
In-depth PII scanning, securing and deletion is an extensive process. Once you have concluded it, you won’t want to do it again for some time.
Thankfully, implementing long-term processes is the perfect way to safeguard sensitive personal data in the long term.
Firstly, you will need to establish your PII data policy. This should include guidelines on what data is collected, how it is stored and for how long.
It also needs to include a data breach response plan and extensive workflows and records for data access. Once complete, update your website’s privacy policy and cookie consents.
You should also have an arsenal of tools at your disposal for handling customer data. DataTrue can be instrumental in helping you maintain compliance with regulations.
Features like Personas help your systems to immediately identify PII and respond accordingly.
When you create a Persona in your DataTrue account, you set up as many fields as you like, including any information relevant to your customer journeys. Perhaps you’re planning to test the checkout process?
A Persona with billing and shipping details ensures your tests have all the information they need. Once the Persona is created, you apply it to any Simulation test you like.
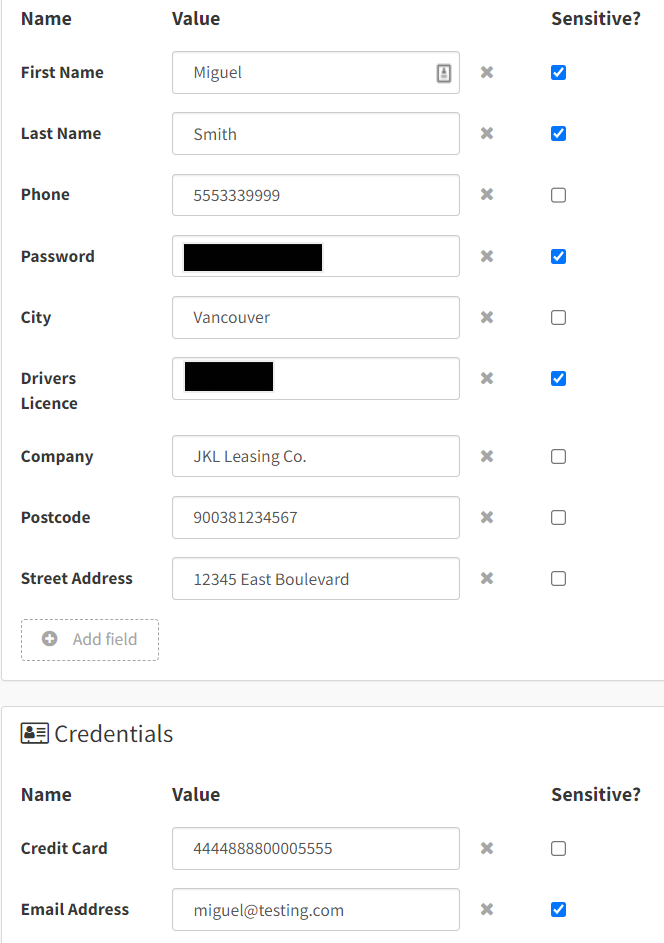
Notice that there’s a “Sensitive” checkbox next to each field. By checking this box, you can tell DataTrue that this information is, well, sensitive, and should trigger an alert if shared. Now you’re ready to test your customers’ experiences and make sure their private information doesn’t leave your site.
Keep PII private with DataTrue
With DataTrue, you’re in control of your data. Tools like Personas, Sensitive Data Alerts, and scheduled tests help ensure that you know about potential issues before they can cause damage. Setting up these tools is straightforward and easy, and our team is ready to help with any questions or advanced implementations you may have.
Book a demo with DataTrue today to discover all the ways it can streamline your business’ approach to data.
Frequently asked questions
What is sensitive PII?
PII is generally categorised as either “sensitive” or “non-sensitive”. Sensitive PII is data that directly identifies an individual and could prove especially harmful in the event of a data breach.
Examples of sensitive PII include:
- Unique identification numbers such as those of driver’s licences and passports
- Biometric data
- Medical information
What is data loss prevention?
Data loss prevention refers to systems and protocols in place to prevent data breaches. It is a critical part of PII security.
It involves security procedures to prevent data breaches, as well as internal processes to ensure staff do not share PII externally or access it inappropriately.
What do you do if you detect PII files on an unprotected computer?
If PII files are detected on an unprotected computer, the easiest option is to delete the data as soon as possible. If the PII is non-essential or can be accessed elsewhere, this is the best option.
Alternatively, you can transfer the data to a secure location. Finally, you could take the necessary steps to protect the computer. This might involve installing software
If you suspect that PII has been involved in any kind of data breach, you must report it to an authority as soon as practicable. In the event of a serious data breach, you may also be required to inform the affected customers.
