If you want to ensure your cookies are operating as intended, as well as maintaining compliance with increasingly stringent data laws, cookie audits are essential. In this article, we’ll share what you need to know about cookie audits, from tools to methods you can use to keep your website analytics firing on all cylinders.
What are cookies and how do they work?
Cookies are short pieces of text sent from a website to a browser that record information about the user. Browsers store cookies, allowing the website to refer back to the information at a later time. Cookies can be used for everything from remembering a user’s preferred language to targeting advertising based on browsing activity.
Here is a brief overview of how cookies work in a technical sense:
- A user’s internet browser sends an access request to a website server
- The server sends the webpage to the browser, including the cookies
- The browser loads the page and receives and stores the cookies
Whether you know it or not, cookies are almost certainly in use on your website. You might not be aware of cookies on your site if they have been installed by your CMS or by third-party sites. Regardless of their source, you are responsible for ensuring their functionality and legal compliance.
There are different types of cookies that serve different purposes.
First-party cookies vs third-party cookies
First-party cookies are generated by the website a user is accessing. These cookies are primarily used for functionality and authentication. For example, a user’s login information can be stored within a cookie, meaning the next time they visit the site, they will not need to log in.
Third-party cookies are cookies generated by other websites. These cookies are used to track certain information across different sites. Third-party cookies are primarily used for the purposes of advertising. For example, your shopping history on a site like Amazon can be captured by third-party cookies, which can then be accessed by different websites to personalise your browsing experience.
Essential cookies vs non-essential cookies
Essential cookies are necessary for the fundamental functionality of a website. If a user chooses to disable these kinds of cookies, their experience of using a website will be negatively affected.
Non-essential cookies can be disallowed by users, and they will not notice any difference in the functionality of a website. Examples of non-essential cookies include third-party tracking cookies or cookies from web analytics tools like Google Analytics.
Session cookies vs persistent cookies
Session cookies are cookies that are automatically deleted when a browsing session ends. They collect information that is not relevant across browsing sessions or websites. For example, when a user fills in a form on a webpage, a short-lived session cookie will remember the information that has been filled in, before deleting it when the session ends.
Persistent cookies are cookies stored on a user’s hard drive for longer periods of time. Persistent cookies can include log-in data and cross-site advertising data. Of these 2 kinds of cookies, persistent cookies are the most likely to collect sensitive data.
What are cookies used for?
Websites use cookies for a wide range of purposes from simple user functionality to the wider marketing aims of a business.
- Functionality cookies – Cookies are used for the fundamental functionality of a website. They make the browsing experience easier and more pleasant. Functionality cookies collect data about user preferences, shopping carts and more.
- Security cookies – Security cookies are used to protect users in a whole range of ways. From login information to authenticating user activity, these types of cookies work to prevent bad actors from acting on behalf of other users for nefarious ends.
- Analytics cookies – Websites utilise analytics cookies to collect information about how users are interacting with their service. These cookies are generally tied in with applications like Google Analytics. Analytics cookies allow websites to see how long users spend on particular pages, or the route customers go through on a website. This enables companies to improve their sites and make them more useful for customers.
- Advertising cookies – Advertising cookies are used for everything from rendering ads to collecting information across websites for the purpose of personalising ad campaigns. Advertising cookies help companies deliver more relevant ads to customers, and allow marketers to analyse the performance of their campaigns.
- Personalisation cookies – Personalisation of the browsing experience goes beyond simply advertising. For example, Google uses cookies to collect data about your precise location, enabling it to show highly relevant results. Sites like YouTube use cookies to offer recommendations about content that is likely to be of interest to the user.
What is a cookie audit?
A cookie audit is a process by which website owners can ensure cookies are effective and legally compliant. It enables you to gain a greater understanding of how your site uses cookies, the data they collect, how long the data is being stored, whether they are secure and much more.
After auditing cookies, you will have a holistic understanding of the role cookies play on your website, and how they can be improved.
There are 2 ways to audit cookies. The first is an automatic cookie audit, done with the help of a cookie audit tool. Alternatively, you can conduct a manual cookie audit using nothing but a browser.
How to conduct an automatic cookie audit
Automatic cookie audits are conducted with cookie audit tools. Tools such as DataTrue can be used to ensure your cookies are legally compliant and properly collect the data you want.
Conducting a cookie audit with DataTrue is simple. Below is a rundown of the elements of a cookie audit with DataTrue, and how each step helps your business.
You can learn more about using DataTrue for cookie audits here. If you want to gain a stronger understanding and control over cookies used on your website, book a demo and find out how you can use DataTrue in your business.
Enhanced cookie discovery
In order to conduct a successful audit, you need to ensure you have captured a wide breadth of cookies on your site. DataTrue uses a range of processes to discover hard-to-find cookies.
DataTrue uses site-wide scans and simulated interactions to find these kinds of cookies. You can also validate the attributes of cookies without the need to script.
Cookie policy audit
DataTrue allows users to define policies for cookies. You can set up a range of different policies allowing and disallowing the use of particular cookies based on location and other user profile factors. Then, you can present your policies to users of your site, allowing them to opt in and out of the use of different cookies.
DataTrue allows you to set cookies on your site as required, allowed or not allowed. You can then set blanket rules either blocking or allowing cookies at scale. If your site policies are breached at any point, you’ll receive an alert, allowing you to quickly respond to any irregularities.
This step is critical to ensuring compliance with rapidly-evolving data compliance laws around the world. Following these laws becomes much simpler with the help of software like DataTrue.
Consent validation
Another facet of DataTrue’s cookie audit tool allows you to configure consent settings to be followed in quality assurance (QA) testing. You can discover any errors in lower development environments. This prevents your users from experiencing issues with your cookies and enables you to avoid any complications with data compliance laws.
DataTrue also provides alerts for any irregularities in the consent manager on your website.
How to conduct a manual cookie audit
Although it can be highly beneficial to leverage automated cookie audits with the help of tools like DataTrue, it is possible to do so without any outside software. The following steps will allow you to conduct a cookie audit using nothing but a standard browser and your personal know-how. Keep in mind that even a perfectly-conducted manual cookie audit can be extremely tedious and incomplete when compared to an automatic audit.
Step 1: Identify cookies
While you can identify cookies using external software, it’s also possible to do so in the developer console of your web browser. This is a time-consuming process, and you should perform it on multiple pages on your website to capture as many cookies as possible. For example, a page on your site that embeds with a third-party service like a video player will contain cookies that cannot be found on other pages.
In order to properly identify cookies, open a private browsing window and close other websites. Ensure any cookie-blocking features on your browser have been disabled. Be advised that even if you follow these steps to a tee, you may still miss some cookies. The best way to capture all cookies on your site is with the help of cookie auditing tools like DataTrue.
Here’s how you can identify cookies in Chrome and Firefox:
How to identify cookies in Chrome
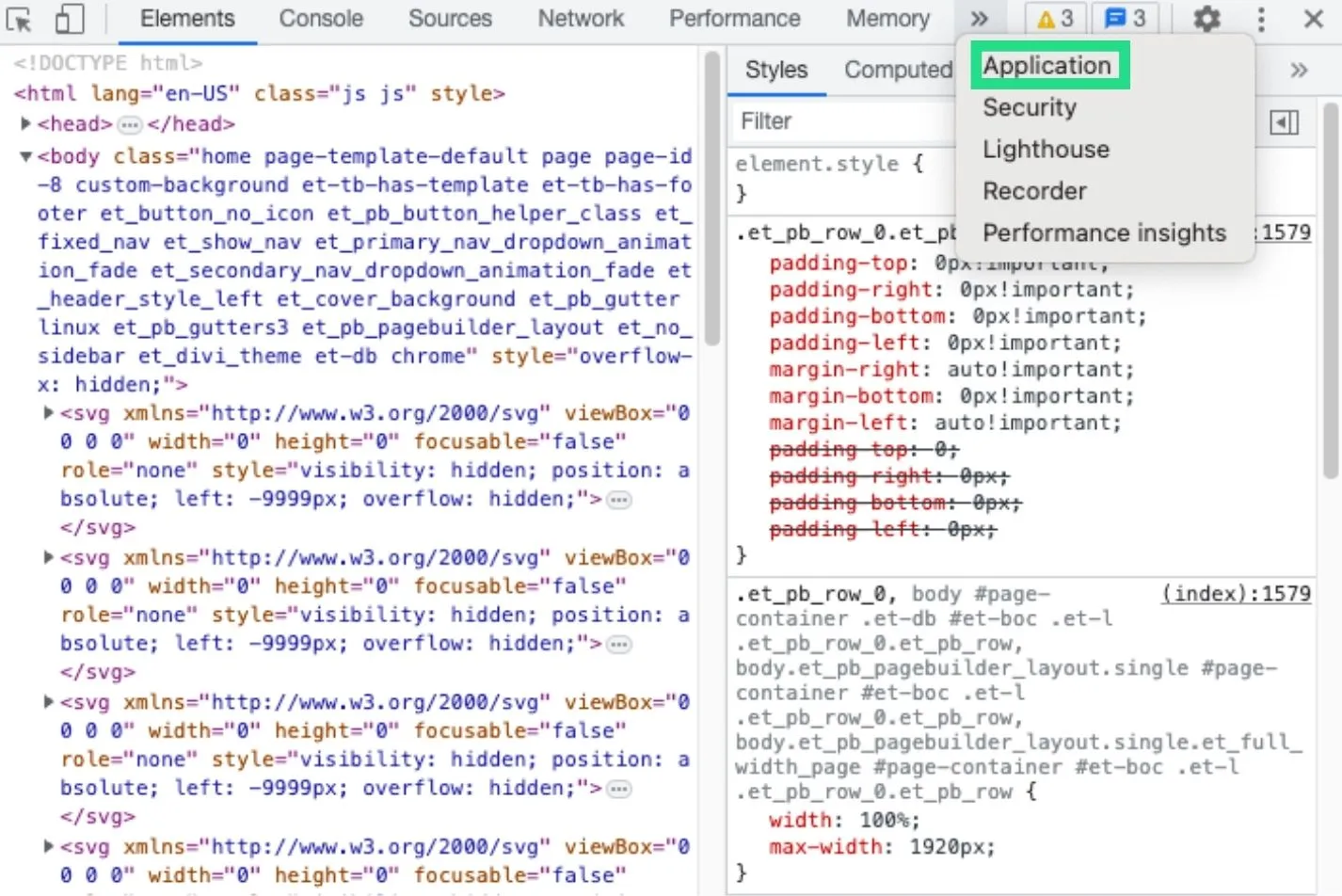
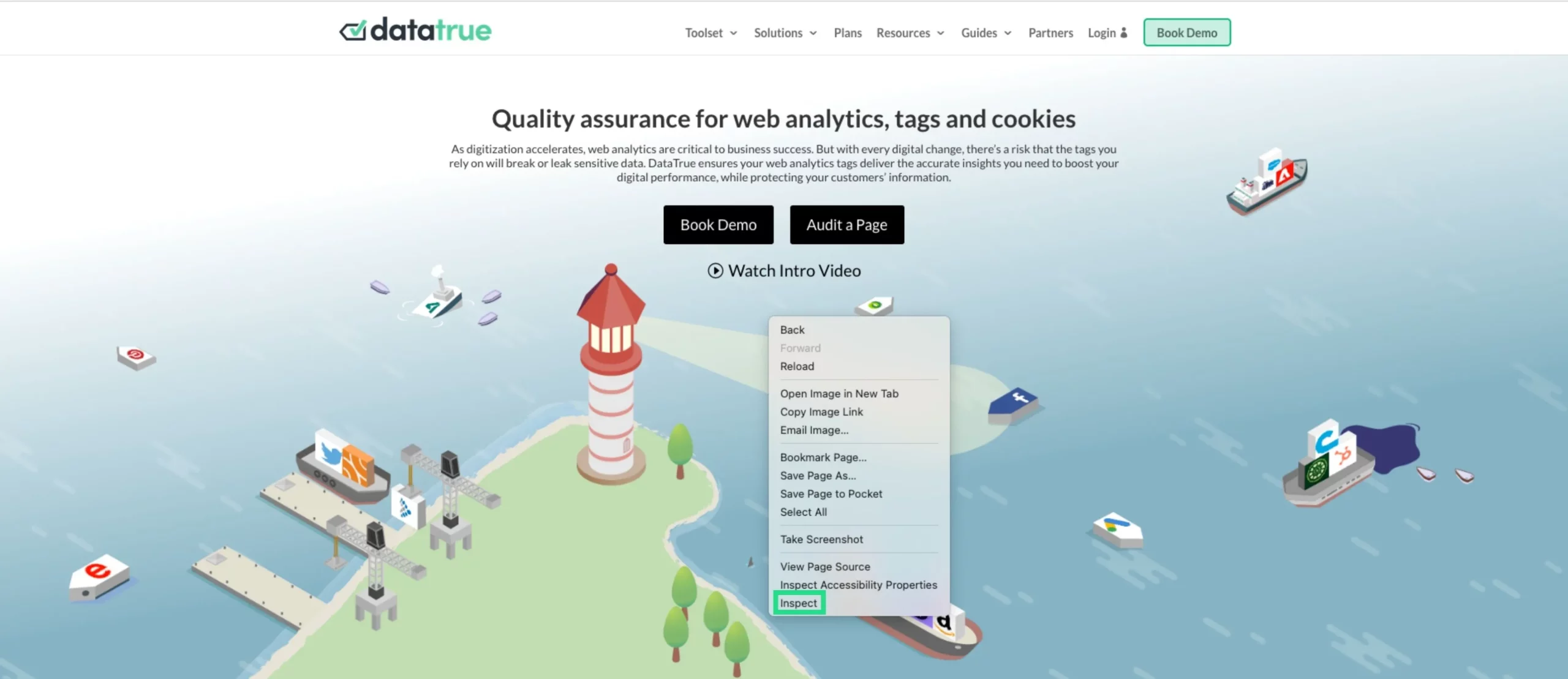
- Right-click on the window of your website and select “Inspect”.
- Select the “Application” tab. This may require you to click on the “>>” option.
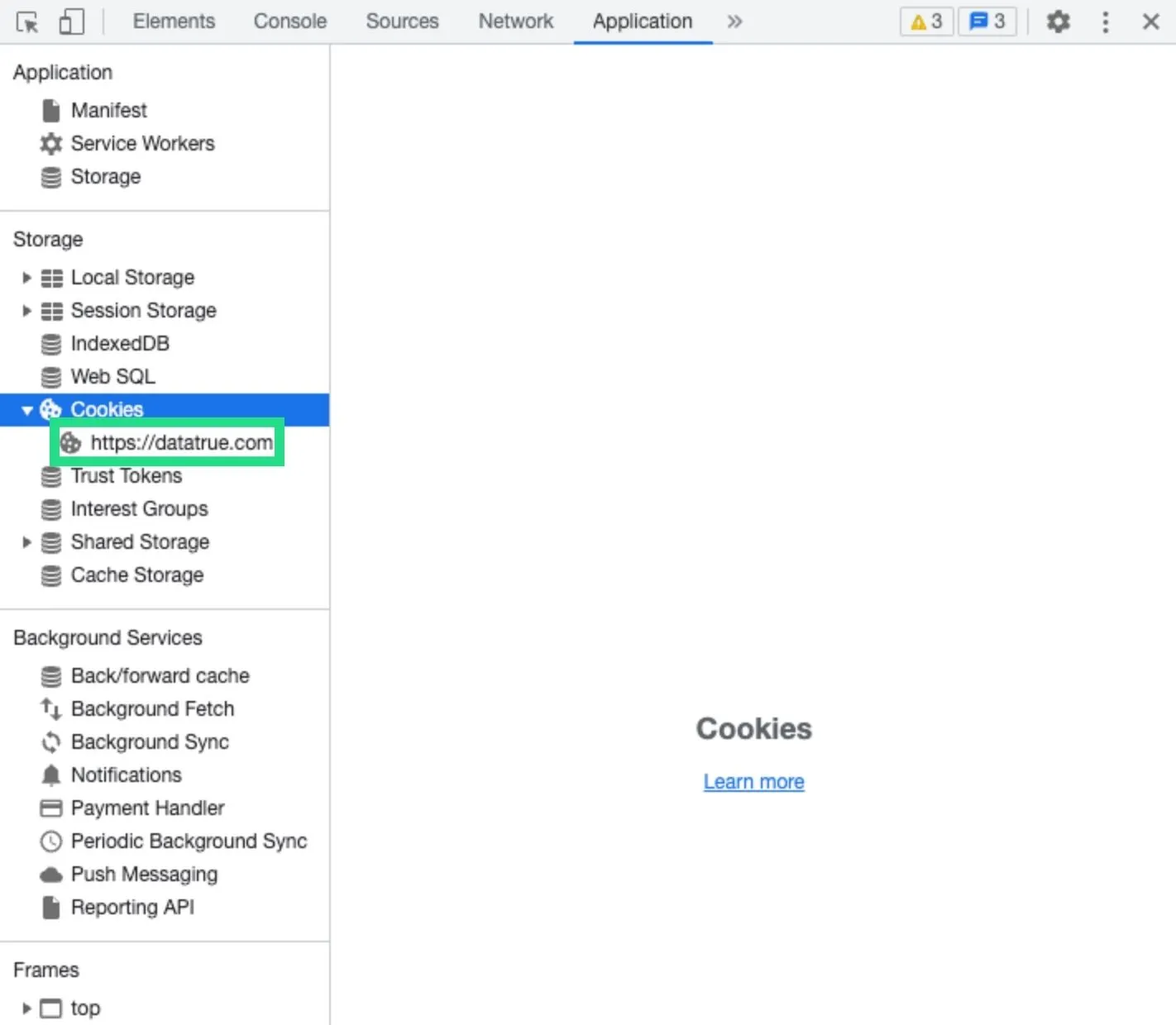
- A sidebar will now appear. Click the drop-down arrow next to “Cookies” and select your domain.
- You will then be able to see the cookies for that webpage, along with some information about each cookie, including the originating domain, expiration date and security.
How to identify cookies in Firefox
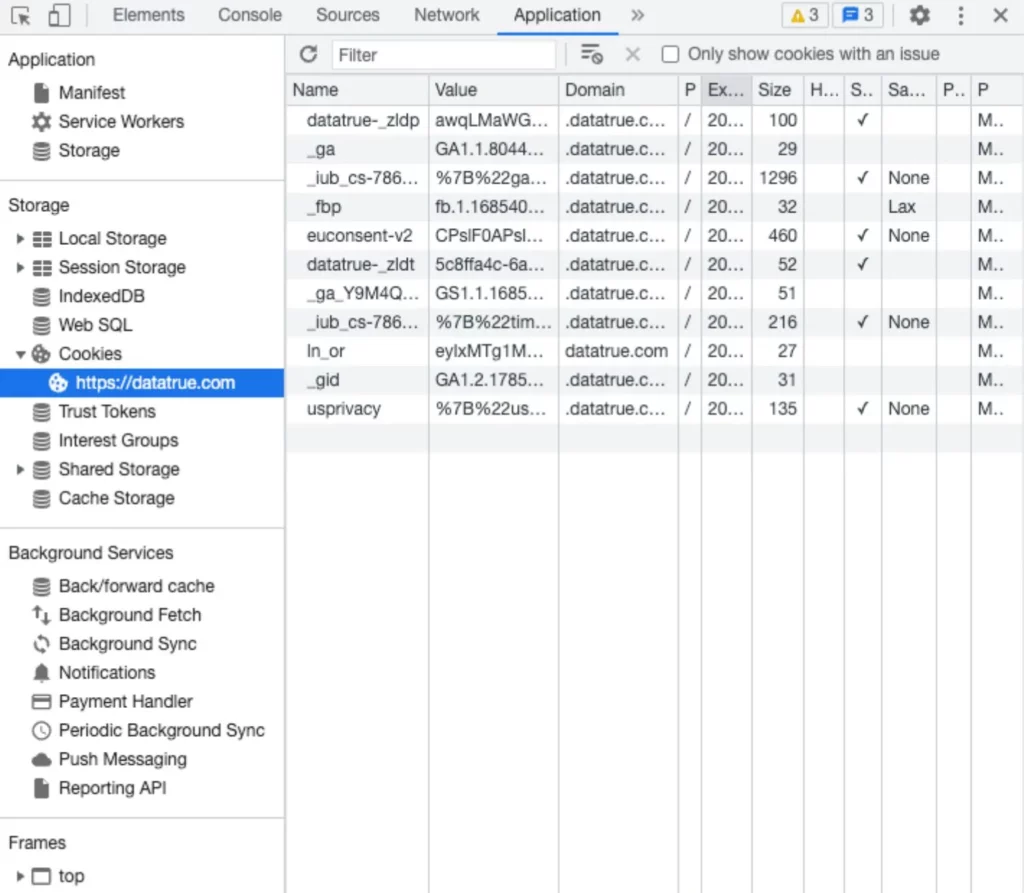
- Right-click on the window of your website and select “Inspect”.
- Select the “Storage” tab.
- A sidebar will now appear. Click the drop-down arrow next to “Cookies” and select your domain.
- You will then be able to see the cookies for that webpage, along with some information about each cookie, including the originating domain, expiration date and security.
Step 2: Conduct a cookie review and analysis
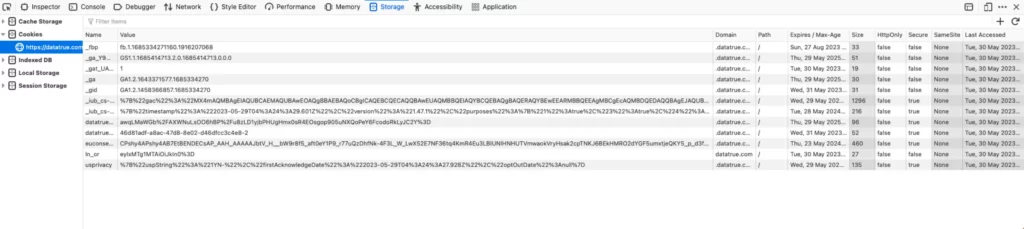
The next step in your manual cookie audit is to analyse the data you’ve just acquired. Here’s a rundown of some of the categories of information you can find in your browser, and how to properly interpret this information:
- Name – The name of a cookie can tell you a lot about it. Simply plugging the name of a commonly-used cookie into Google will quickly yield results including the functionality and purpose of that cookie.
- Domain – This field lets you know about the original domain of the cookie.
- Expires/Max Age – This field usually either displays “Session”, or a specific date and time when a cookie will be automatically deleted from a user’s browser.
- Size – This refers to the storage size of the cookie, measured in bytes. Use this field to ensure the total size of cookies on your site does not exceed the recommended maximum of 4,096 bytes.
- Secure – A cookie that is ticked as secure will only be sent on the more secure HTTPS connection, rather than the less secure HTTP connection.
Step 3: Categorise cookies
Once you have established an understanding of your website’s cookies, you must categorise them. This is a critical step, as your categories of cookies will eventually be presented to your users so they may opt out of them.
The most important cookie categories to note here are essential and non-essential cookies. Under even the most stringent data laws, it is generally not necessary to offer customers the opportunity to opt out of essential cookies. However, users must have the opportunity to opt out of non-essential cookies.
You can categorise with as much specificity as you like. For example, breaking out non-essential cookies into categories like advertising, geolocation, analytics and more will give your customers greater control over their privacy and browsing experience.
Step 4: Ensure compliance
The next step in your manual cookie audit is to ensure your cookie setup is compliant with data laws around the world. You should be aware of data laws in all jurisdictions in which your website is accessible, but there are 2 jurisdictions that are of particular interest to website owners. The European Union applies the General Data Protection Regulation and ePrivacy Directive (also known as the EU cookie law), while California applies the California Consumer Privacy Act.
These jurisdictions contain a combined population of over 500 million potential website visitors and customers. They are also 2 of the most stringent policies in the world. You should familiarise yourself with these policies in-depth before undertaking a manual cookie audit. Here are some broad steps you can take to in order to comply with these laws:
- Clearly and comprehensively explain which cookies are used on your website, how they are used.
- Disclose if data collected by cookies may be sold to a third party.
- Obtain prior consent before storing non-essential cookies on a user’s device.
- Give users the ability to opt out of non-essential cookies at any time.
Step 5: Create a cookie policy
Now that you have a stronger understanding of the cookies on your website, you can create your cookie policy. Your cookie policy should consist of a top-level document that outlines how cookies are used on your website and a range of smaller policies allowing customers to opt out of particular cookies.
You can access cookie policy templates online. Remember that your cookie policy is a legal document, so take great care in its creation.
You’ll then need to implement your policy on your website. Most commonly, this is done with the creation of a cookie banner pop-up presented to users upon arrival on your website.
Step 6: Implement a long-term cookie management strategy
Keeping track of your cookie usage is a never-ending battle. The following steps will ensure you maintain compliant and effective cookies into the future.
- Schedule frequent, repeated cookie audits and ensure you can identify data privacy leaks straight away.
- Stay abreast of developments in data privacy legislation.
- Regularly review your cookie and consent management policies to ensure your users are always in the best position to maintain their privacy and enjoy all the functionality of your website.
Automatic cookie audit vs manual cookie audit
Now you know how to conduct a cookie audit in both an automatic and manual manner.
While it is possible to conduct an analysis of your cookies and create a comprehensive cookie policy by yourself, it isn’t an easy undertaking by any means. It is also possible to miss out on particular cookies in this process, leading to inaccurate cookie policies. The creation of cookie policies themselves is a complex task with legal ramifications, so undertaking it without the assistance of cookie audit tools is potentially risky.
As such, it is a sound idea to use a cookie audit tool like DataTrue to assist in the complex task of a cookie audit, especially if you lack in-depth legal and technical expertise. DataTrue also offers a holistic approach to data management to ensure your site is legally compliant and utilises the most accurate information possible.